The relevant formula is the Stefan-Boltzman formula:
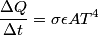 Here, 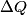 / /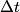 is the rate at which energy is radiated from the blackbody, is the rate at which energy is radiated from the blackbody, 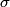 is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant, is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant,  is the emissivity of the blackbody (which is equal to 1 for an ideal Blackbody), is the emissivity of the blackbody (which is equal to 1 for an ideal Blackbody), 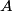 is the area of the blackbody, and is the area of the blackbody, and 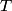 is the temperature in Kelvin. is the temperature in Kelvin.Replacing 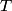 by by 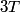 therefore increases the rate at which energy is radiated by a factor of therefore increases the rate at which energy is radiated by a factor of 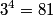 . So, answer (E) is correct. . So, answer (E) is correct. |